摘要:目的? 观察黄芪多糖联合二甲双胍对衰老2型糖尿病模型小鼠肝脏糖脂代谢的影响,探讨其作用机制。方法? 采用高糖高脂饲料联合链脲佐菌素诱导自然衰老小鼠制作衰老2型糖尿病小鼠模型。实验小鼠分为衰老对照组、衰老糖尿病模型组、二甲双胍治疗组、黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组,各给药组给予相应药物灌胃,连续60 d。测定小鼠体质量、摄食、饮水、空腹血糖变化,HE染色观察小鼠肝组织形态学,糖原染色和油红O染色观察肝组织糖脂代谢,透射电子显微镜观察小鼠肝组织细胞超微形态。结果 ?与衰老对照组比较,衰老糖尿病模型组空腹血糖明显升高、体质量减轻、摄食和饮水明显增加(P<0.05)。与衰老糖尿病模型组比较,各给药组空腹血糖明显降低、体质量增加、摄食和饮水明显减少(P<0.05)。HE染色显示,与衰老对照组比较,衰老糖尿病模型组肝组织病变、坏死严重,各给药组较模型组明显改善,其中黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组肝组织结构改善最明显。糖原染色与油红O染色显示,衰老对照組糖原、脂滴含量较少,衰老糖尿病模型组糖原、脂滴含量明显增多;与衰老糖尿病模型组比较,各给药组小鼠肝组织糖原和脂滴含量均显著减少(P<0.05),且黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组效果更明显。透射电镜观察显示,衰老糖尿病模型组较衰老对照组肝组织细胞线粒体、内质网损伤严重,各治疗组较模型组明显缓解,且黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组效果更明显。结论? 黄芪多糖+二甲双胍可通过对肝组织细胞线粒体及内质网的保护作用,改善衰老2型糖尿病小鼠模型的肝脏糖脂代谢。
关键词:衰老2型糖尿病;二甲双胍;黄芪多糖;肝脏;糖脂代谢;小鼠
中图分类号:R285.5 ???文献标识码:A??? 文章编号:1005-5304(2019)02-0047-05
DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-5304.2019.02.011
开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):
Abstract: Objective To observe the effects of astragalus polysaccharides combined with metformin on liver glucose and lipid metabolism in aging type 2 diabetic mice; To discuss the mechanism of action. Methods The models of aging type 2 diabetic mice were induced by high sugar and high fat diet combined with streptozotocin in natural aging mice. The experimental mice were divided into aging control group, aging diabetic model group, metformin treatment group and astragalus polysaccharides combined with metformin treatment group. Each administration group was given the corresponding medicine for gavage for 60 days. The changes of body weight, feeding, drinking water and fasting blood glucose were measured in each group. The morphological changes of liver tissues were observed by HE staining. Glycogen staining and oil red O staining were performed to observe the glycolipid metabolism of liver tissue. Transmission electron microscopy was used to observe the ultrastructural changes of liver cells. Results Compared with the aging control group, the fasting blood glucose increased significantly, the body weight decreased and the feeding and drinking water increased significantly in the aging diabetic model group (P<0.05). Compared with the aging diabetic model group, the fasting blood glucose decreased significantly, the body weight increased, and the feeding and drinking water decreased significantly in each administration group (P<0.05). HE staining showed that compared with the aging control group, pathological changes and necrosis of the liver tissue in the aging diabetic model group were more serious, but the administration groups were significantly improved compared with the model group. The improvement of liver tissue structures in astragalus polysaccharides combined with metformin treatment group was the most obvious. Glycogen staining and oil red O staining showed that the contents of glycogen and lipid droplets in the aging control group were fewer, and the contents of glycogen and lipid droplets in the aging diabetic model group increased significantly (P<0.05). Compared with the aging diabetic model group, the contents of glycogen and lipid droplets in the liver tissues of the administration groups were significantly reduced (P<0.05), and in the astragalus polysaccharide combined with metformin treatment group, the reductions were more obvious. Transmission electron microscopy showed that the mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum in the liver tissue of the aging diabetic model group had more damage rather than those in the aging control group, and the administration groups were significantly relieved compared with the aging model group, and the effects of astragalus polysaccharide combined with metformin were better. Conclusion Astragalus polysaccharide combined with metformin can improve glucose and lipid metabolism of liver in aging type 2 diabetic mice models by protecting liver mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum.
Keywords: aging type 2 diabetes; metformin; astragalus polysaccharides; liver; glucose and lipid metabolism; mice
随着年龄增长,机体常伴随一系列生理和病理改变。其中2型糖尿病已成为老年人死亡的主要病因。目前治疗糖尿病的常用药物为二甲双胍,但临床发现,该药在治疗中存在单纯用药疗效不佳,可能引起消化不良和低血糖等不良反应[1]。中医认为2型糖尿病因“脾虚肝郁、氣血两虚”所致,其中“脾虚肝郁”影响更大[2]。黄芪具有补气健脾、抗衰老的功效,研究发现黄芪多糖具有调节免疫、提高胰岛素分泌、减缓胰岛素抵抗的作用[3-5]。本研究采用黄芪多糖联合二甲双胍作用于衰老2型糖尿病小鼠模型,从肝脏糖脂代谢入手,探讨黄芪多糖对衰老糖尿病的治疗机制,为其临床应用提供依据。
1? 实验材料
1.1? 动物
雄性5月龄SPF级昆明种小鼠50只,甘肃中医药大学科研实验动物中心,动物合格证号SCXK(甘)2015-0002。饲养于温度20~25 ℃、相对湿度40%~70%环境,每日光照12 h,自由摄食饮水。
1.2? 药物
黄芪多糖,上海索莱宝生物科技有限公司,批号608B031;盐酸二甲双胍片,上海源叶生物科技有限公司,批号S24O8G46081。
1.3 ?主要试剂与仪器
链脲佐菌素(STZ),美国Sigma公司;多聚甲醛,中国Biosharp公司;25%戊二醛溶液,美国Sigma公司;HE染色试剂盒、PAS染色试剂盒、油红O染液,中国索莱宝公司。美国罗氏活力型血糖仪、罗氏血糖试纸,德国Roche公司;光学显微镜,日本Olympus公司;透射电子显微镜,日本JEOL公司。
1.4? 造模及分组
将50只小鼠随机分为衰老对照组12只,衰老糖尿病造模组38只。衰老对照组给予普通饲料喂养。衰老糖尿病造模参照文献[6],采用腹腔注射STZ制作糖尿病模型,先用高糖高脂饲料连续喂养小鼠4周,然后每只小鼠连续3 d腹腔注射70 mg/kg STZ,以连续2次空腹血糖≥16.7 mmol/L为造模成功。造模4周后,衰老对照组小鼠死亡1只;衰老糖尿病模型造模成功33只,将其随机分为衰老糖尿病模型组、二甲双胍治疗组和黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组,每组11只。
1.5? 给药
二甲双胍用去离子水配制成100 g/L水溶液,按10 mL/(kg·d)灌胃二甲双胍治疗组小鼠;黄芪多糖配制成300 g/L水溶液,与100 g/L二甲双胍等体积混合,按10 mL/(kg·d)灌胃黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组小鼠;衰老对照组和衰老糖尿病模型组小鼠给予等量生理盐水灌胃。每日1次,连续60 d。其中衰老糖尿病模型组有小鼠死亡,为便于统计分析,治疗后以每组8只小鼠进行分析。
1.6? 一般状况测定
小鼠适应性喂养1周,每周测定小鼠体质量、摄食、饮水、空腹血糖(每次测量前禁食12 h)。
1.7? 肝组织形态观察
小鼠断颈处死后,摘取小鼠肝脏,生理盐水漂洗干净、滤纸吸干,选取一小叶,4%多聚甲醛浸泡,室温固定,石蜡包埋,切片(厚约3 μm),脱蜡、水洗后HE染色,封片后显微镜观察。
1.8? 肝糖原染色检测
取包埋好的组织蜡块,切片(厚约3 μm),进行肝糖原PAS染色,显微镜观察肝糖原含量。
1.9? 肝脂滴含量检测
小鼠断颈处死,摘取肝脏,移至1.5 mL冻存管中,置于液氮中冰冻,-80 ℃冰箱保存。取冻存的肝脏,制成6 μm厚的冰冻切片,并于室温下进行油红O染色、异丙醇漂洗、苏木素复染、中性甘油封片后镜下观察,并统计肝脂滴的面积,分析脂滴沉积量。
1.10? 肝脏透射电镜观察
将漂洗、吸干后肝脏修成大约1 mm3的小块,放入4 ℃预冷的2.5%戊二醛溶液中过夜固定,PBS漂洗3次,1%锇酸染色、脱水、浸透、包埋、聚合后修块,切成70 nm的薄片,复染后透射电子显微镜观察并拍照。
1.11? 统计学方法
采用SPSS21.0统计软件进行分析,Image J软件进行光密度分析。计量资料以±s表示,各组间比较用方差分析。P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。
2? 结果
2.1? 一般状况结果
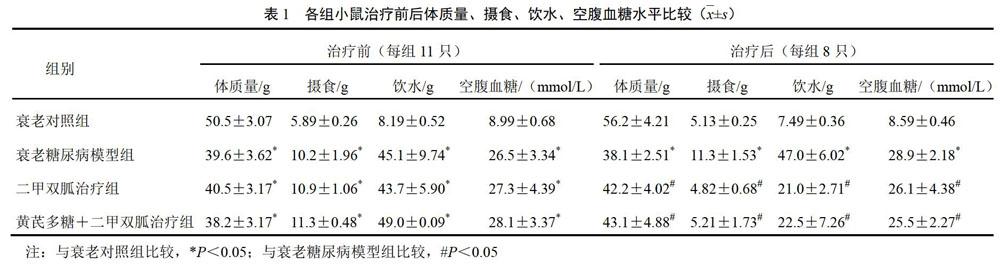
衰老糖尿病造模组较衰老对照组有明显的“三多一少”症状,即摄食、饮水、空腹血糖明显增加,而体质量显著降低;治疗后小鼠体质量升高,摄食、饮水、空腹血糖较模型组明显下降( P<0.05);且黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组体质量、摄食、饮水、空腹血糖变化较二甲双胍治疗组更明显。结果见表1。
2.2? 肝组织HE染色结果
衰老对照组小鼠肝组织结构基本正常,只在中央静脉区有轻度的排列疏松并伴有轻度的气球样变;衰老糖尿病模型组小鼠肝组织细胞排列紊乱,有弥漫性肝细胞水肿,变性、坏死、气球样变,并伴有肝窦、肝静脉淤血;二甲双胍治疗组小鼠肝组织细胞排列疏松,较模型组细胞水肿、变性减轻;黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组小鼠肝组织细胞排列较衰老糖尿病模型组整齐,细胞水肿、变性明显减轻。2.3? 肝糖原PAS染色结果
衰老对照组小鼠肝糖原颗粒染色较浅且数量较少;衰老糖尿病模型组小鼠肝糖原明显增多,呈弥漫性分布。二甲双胍治疗组和黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组小鼠较衰老糖尿病模型组肝糖原均减少,其中黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组肝糖原减少更显著。
2.4? 肝组织脂滴代谢变化
各组小鼠肝脏冰冻切片油红O染色结果显示,衰老对照组肝组织中脂滴较少,衰老糖尿病模型组肝组织中脂滴含量明显增多,且体积较大、染色较深。各治疗组肝组织中脂滴含量较衰老糖尿病模型组均显著减少(P<0.05)。
2.5? 肝组织透射电镜观察结果
电镜观察显示,衰老对照组小鼠肝细胞有退化的趋向,胞质中有脂褐素颗粒沉积,部分线粒体有轻度肿胀,内质网排列规则,形态正常;衰老糖尿病模型组小鼠肝细胞核皱缩显著,核膜明显不规则,出现线粒体融合,较多线粒体呈“管状”和“空泡状”,内质网肿胀、结构紊乱;二甲双胍治疗组肝细胞核膜较完整,轻度皱缩,线粒体、内质网肿胀程度较衰老糖尿病模型组减轻;黄芪多糖+二甲双胍治疗组肝细胞核较衰老糖尿病模型组完整,皱缩不明显,线粒体肿胀程度较衰老糖尿病模型组和二甲双胍治疗组减轻,未见空泡,内质网排列也规则,扩张程度减轻。此外,电镜观察还发现衰老糖尿病模型组肝血窦间隙明显扩张,治疗后肝血窦扩张程度减轻。
3? 讨论
衰老是糖尿病发病的重要诱因,年龄超过60岁的人群中,基础血糖会升高10%以上,随着年龄增加,脂肪也重新分布,胰岛素抵抗更为明显。而且老年性糖尿病患者常有病情复杂、合并症多、糖尿病症状不典型等特点。
有研究利用D-半乳糖诱导小鼠衰老进行造模[7-8],但刘克明等[9]报道自然衰老小鼠存在明显的免疫功能降低、学习行为能力降低等特点,而D-半乳糖致衰老对小鼠体内的代谢环境进行了人为干预,尚不能完全反映衰老的生理生化改变。因此,本实验利用自然衰老小鼠进行造模,可更真实反映机体生理代谢变化。有报道,通过高糖高脂饲料与小剂量STZ进行糖尿病模型的复制成功率可达80%[10]。经本研究复制,模型小鼠出现明显的“三高一低”糖尿病特征,造模成功率较高。但由于本研究采用的小鼠为衰老小鼠,其基础体征较差,较之前的报道后期死亡率较高,这也正反映了糖尿病合并衰老疾病模型的特异性。
以高血糖为特征的糖脂代谢紊乱为糖尿病的发病基础。肝脏是糖脂代谢的重要场所,肝细胞含有大量线粒体及内质网,可使肝细胞对葡萄糖摄取、利用增加,代谢加快,并转化为肝糖原贮存在肝组织。通过二甲双胍单独治疗及与黄芪多糖联合治疗后,小鼠肝组织病理结构、糖原染色和脂滴含量均较衰老糖尿病模型组有明显改善。而且联合用药组改善情况较优于单独用药组,表明黄芪多糖联合二甲双胍对肝组织结构有一定的保护作用,并可调节肝组织糖脂代谢紊乱。本研究通过进一步电镜观察发现,该调节作用可能与药物作用保护肝组织细胞中线粒体和内质网的结构有关。各治疗组较衰老糖尿病模型组线粒体肿胀和内质网扩张明显减轻。本研究结果显示,随着2型糖尿病合并衰老的发生,线粒体形态改变和内质网应激不断加重,糖原及脂滴的沉积增加,肝组织病变也进一步恶化。黄芪多糖联合二甲双胍可通过调节细胞内的线粒体途径和内质网应激起到改善肝脏糖脂代谢的作用。
Novelle等[11]发现,二甲双胍通過抑制线粒体复合酶Ⅰ的活性来降低ATP水平,其通过调节葡萄糖转运蛋白和糖酵解酶的表达来影响线粒体呼吸链,从而改善肝脏脂肪变性及炎性反应。研究发现,黄芪多糖可抑制由肝细胞内质网压力引起的活化转录因子6的活性,增加2型糖尿病大鼠肝组织AMPK磷酸化水平,从而提高大鼠胰岛素敏感性,增加大鼠对高血糖症和口服葡萄糖的耐受性[12]。
综上所述,本实验通过分析肝脏病理形态、糖脂代谢变化及电镜观察,发现黄芪多糖联合二甲双胍可通过改善肝脏糖脂代谢对衰老2型糖尿病小鼠有一定的治疗作用,为探讨衰老2型糖尿病治疗的方法及思路提供了依据。
参考文献:
[1] YEHUDA A B, ZINGER A. The older patient with diabetes: a practical approach[J]. Diabetes/metabolism Research & Reviews, 2014,30(2):88-95.
[2] 李永民,李建东,杨洁,等.中药糖平煎对实验性2型糖尿病治疗机理的研究[C]//中华中医药学会内科分会消渴病学术研讨会,2003.
[3] 毛竹君,寿旦,柴可夫.黄芪多糖小檗碱下调IR-INS-1细胞miR-126-3p改善胰岛素抵抗[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(7):2961-2965.
[4] 唐思梦,杨泽民,陈伟强,等.黄芪多糖保护胰岛β细胞改善大鼠2型糖尿病[J].第二军医大学学报,2017,38(4):482-487.
[5] 胡彩虹,徐坤,孙静,等.黄芪多糖对老年糖尿病大鼠糖脂代谢的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(6):1453-1455.
[6] 许芳芳,王楠,李刚强,等.2型糖尿病小鼠模型的建立与评价[J].中国医学科学院学报,2017,39(3):324-329.
[7] 王晶,黄勇,李海龙,等.党参水提物对D-半乳糖致衰老小鼠肾组织microRNA表达谱的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2016,23(5):69-72.
[8] 章常华,刘彤彤,邓可众,等.黄芩-黄连药对防治D-半乳糖痴呆小鼠的作用机制[J].中成药,2018,40(3):524-529.
[9] 刘克明,王春花,李国星,等.D-半乳糖模型鼠与自然衰老鼠的比较研究[J].卫生研究,2007(6):685-688.
[10] 黄桂红,陈薇,罗昱澜.链脲佐菌素稳定性对诱导糖尿病小鼠模型的影响[J].华夏医学,2009,22(2):201-203.
[11] NOVELLE M G, ALI A, DIEGUEZ C, et al. Metformin:A hopeful promise in aging research[J]. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine,2016,6(3):a025932.
[12] 常越,徐姣,闫嵩,等.黄芪六一汤对2型糖尿病治疗效果的转录组学研究[J].中国中药杂志,2017,42(14):2760-2766.
- 企业财务成本核算信息系统的应用
- 论财务管理在企业内控中的作用与应用
- 浅析财务管理中会计审核的作用
- 会计信息质量在企业管理中的重要作用
- 增值税时代财税融合重点问题探讨
- 中小商业地产企业会计核算应关注的问题
- 浅谈财务公司外汇业务风险管理
- 营改增背景下企业财务管理应对策略研究
- 企业会计监管体系问题探究
- 浅析商业地产企业增值税纳税筹划现状及对策
- 营改增对企业财务的影响及对策分析
- IT视角下管理会计与财务会计的融合研究
- 试论企业内部财务控制的策略
- 浅析“营改增”对我国现代物流企业的影响
- XX乳业财务问题分析
- 企业投资效率角度下提高会计信息质量的方法
- 关于会计职业道德的探讨
- 税务会计原则、财务会计原则的比较与思考
- 财务共享模式下基于电子发票应用的“税企互联”平台构建
- 中小企业财务管理中的问题分析
- “营改增”带来的机遇与挑战
- 互联网时代下会计行业面临的挑战与机遇
- 基于因子分析法的我国商业银行的财务评价
- 电子商务中市场营销策略与运作探讨
- 地方茶叶的电子商务现状及营销策略建议
- interpolishing
- inter-polishing
- interpollinate
- inter-pollinated
- interpollinated
- interpollinates
- inter-pollinates
- interpollinating
- inter-pollinating
- interpols
- interpopulation
- interpour
- interpoured
- interpouring
- interpours
- interpressure
- interpret
- interpretabilities
- interpretable
- interpretablenesses
- interpretably
- interpretation
- interpretational
- interpretations
- interpretative
- 翻穿皮袄过草原
- 翻章
- 翻章子
- 翻筋斗
- 翻筋斗翻斤斗
- 翻箱倒柜
- 翻箱倒笼
- 翻箱倒箧
- 翻箱底亮嫁妆
- 翻绎
- 翻经子
- 翻羹
- 翻羽
- 翻翁
- 翻翔
- 翻翻
- 翻老套
- 翻老婆舌
- 翻老帐
- 翻老底
- 翻老底儿
- 翻老皇历
- 翻老账
- 翻耕
- 翻耕土地