


关键词: 自然语言处理; 中文分词; 神经网络; 双向长短时记忆条件随机场; 字嵌入; 序列标注
中图分类号: TN711?34; TP391.1 ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 文献标识码: A ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?文章编号: 1004?373X(2019)01?0095?05
Abstract: The mainstream Chinese word segmentation method based on supervised learning algorithm requires a lot of corpora labeled manually, and the extracted local feature has sparse problem. Therefore, a bidirectional long short?term memory conditional random field (BI_LSTM_CRF) model is proposed, which can automatically learn the text features, and model the text context dependent information. The tag information before and after sentence character is considered in CRF layer, and the text information is deduced. The word segmentation model has achieved perfect word segmentation results on datasets of MSRA, PKU and CTB 6.0, and the experiment for the model is carried out with news data, MicroBlog data, automobile forum data and restaurant review data. The experimental results show that the BI_LSTM_CRF model has high word segmentation performance in testing set, and strong generalization ability in cross?domain data testing.
Keywords: natural language processing; Chinese word segmentation; neural network; bidirectional long short?term memory random field; word embedding; sequence labeling0 ?引 ?言
中文分词是中文自然语言处理必需的过程,是进一步进行词性标注、机器翻译、信息检索的基础。分词效果直接影响着中文自然语言任务结果的好坏,所以中文分词具有重要意义。然而中文是一种复杂的语言,存在一词多意、未登录词、语句歧义现象,只有结合上下文信息才能有效地进行分词。近些年,中文分词研究取得了持续发展。中文分词常用的方法可以分为以下几大类:基于规则和字典的方法、基于统计的方法、基于神经网络的方法。
基于规则和字典的方法主要思想是建立一个充分大的词典,按照一定的算法策略将待分词的字符序列与词典中收录的词条进行匹配,若在词典中存在,则匹配成功,完成分词[1]。但其对词典依赖性很强,对歧义和未登录词识别效果不佳等问题。基于统计的方法是基于训练语料库来学习任意字符相邻出现的概率,得到分词模型,通过计算字符序列切分最大概率作为分词结果[2]。该方法需要人工定义和提取特征,其性能也受到训练语料、特征设定的影响,存在特征过多、模型复杂、容易过拟合的问题。随着深度学习的快速发展,近年来神经网络算法被广泛用于自然语言处理任务中。由于神经网络可以从原始数据中自主学习特征,不仅替代了人工提取特征的工作量,同时也避免了人为特征设定的局限性。
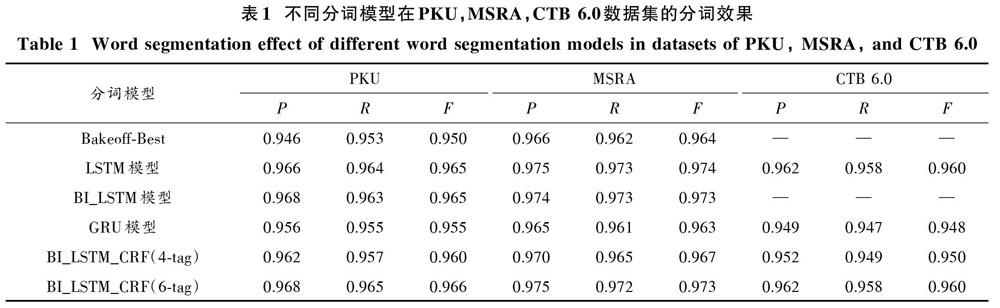
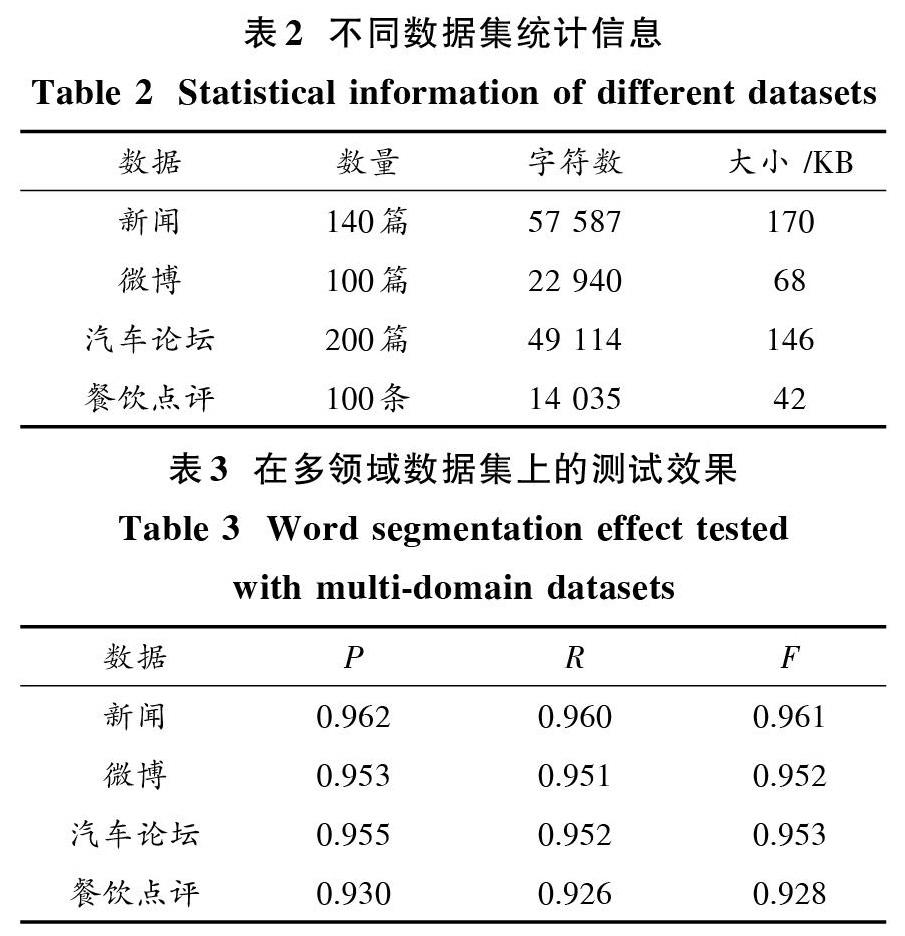
为了提高中文分词的性能,应用BI_LSTM_CRF神经网络处理中文分词任务,使用BI_LSTM_CRF网络构造更具表征的字符信息,本文系统性地比较了4字词位标注与6字词位标注方法在测试集上的测试结果,实验结果表明采用6字词位标注的方法能更好地表征词语中的词位信息,并且性能更加优越。使用6字词位标注方法的神经网络分词模型分别在新闻数据、微博数据、汽车论坛数据、餐饮点评数据进行了测试,实验结果显示,BI_LSTM_CRF神经网络分词模型在跨领域数据测试上也有很好的泛化能力。1 ?神经网络模型在自然语言处理领域中的应用
长短时记忆(Long Short?term Memory,LSTM)网络是递归神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network,RNN)的一种变种,在很多任务上表现的比RNN更好,可以学习长期依赖信息。1997年,Schuster等人在LSTM网络模型基础上提出了双向长短时记忆(Bidirectional Recurrent Neural Networks,BI_RNN)模型,由于是双向输入,在记忆长时信息方面比LSTM更具有优势。以上述神经网络为基础的模型在处理与时间相关的序列任务中取得了很大的成功,通常模型都能对长短时依赖信息进行表达。
文献[3]对神经网络建立概率语言模型,该方法对n?gram模型有显著的改进,并且利用了较长的上下文信息。文献[4]使用神经网络结构处理中文自然语言任务,描述了一种感知器训练神经网络的替代算法,以加速整个训练过程。文献[5]将LSTM网络模型应用于中文分词中,以解决上下文长距离依赖关系,并取得了不错的分词效果。2016年,Yao等人提出采用BI_LSTM网络模型处理中文分词,该模型将过去和未来上下文中文信息都考虑进去,中文分词效果得到了提高。2017年,李雪莲等针对LSTM神经网络模型复杂、训练时间长等问题,提出基于GRU(Gate Recurrent Unit)模型,使得模型训练更加简化并且取得了与LSTM模型相当的分词效果。



4 ?結 ?论
本文主要研究了BI_LSTM_CRF神经网络来实现中文分词,实验中不仅使用MSRA,PKU,CTB 6.0数据集做了测试,比较了4词位标注与6词位标注模型的表现性能,实验结果显示6词位标注模型表现出了更好的分词性能。同时,采用6词位标注的模型对新闻数据、微博数据、汽车论坛数据、餐饮点评数据不同领域进行了测试,结果表明6词位标注的模型在跨领域中文分词也具有良好的性能,说明模型具有很好的泛化能力。
注:本文通讯作者为李晗静。
参考文献
[1] WU A. Word segmentation in sentence analysis [C]// Procee?dings of 1998 International Conference on Chinese Information Processing. Beijing: Chinese Information Society, 1998: 1?10.
[2] LAFFERTY J D, MCCALLUM A, PEREIRA F C N. Conditional random fields: probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data [C]// Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning. San Francisco: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 2001: 282?289.
[3] BENGIO Y, VINCENT P, JANVIN C. A neural probabilistic language model [J]. Journal of machine learning research, 2003, 3(6): 1137?1155.
[4] ZHENG X, CHEN H, XU T. Deep learning for Chinese word segmentation and POS tagging [C]// 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Seattle: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2013: 647?657.
[5] CHEN X, QIU X, ZHU C, et al. Long short?term memory neural networks for Chinese word segmentation [C]// 2015 Confe?rence on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [S.l.: s.n.], 2015: 1197?1206.
[6] GRAVES A. Long short?term memory [M]// Anon. Supervised sequence labelling with recurrent neural networks. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 37?45.
[7] ZHAO H, HUANG C N, LI M, et al. An improved Chinese word segmentation system with conditional random field [C]// Proceedings of the Fifth Sighan Workshop on Chinese Language Processing. [S.l.: s.n.], 2006: 162?165.
[8] MIKOLOV T, CHEN K, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space [EB/OL]. [2013?09?07]. http://www.surdeanu.info/mihai/teaching/ista555?spring15/readings/mikolov2013.pdf.
[9] LAI S, LIU K, HE S, et al. How to generate a good word embedding [J]. IEEE intelligent systems, 2016, 31(6): 5?14.
[10] YAO Y, HUANG Z. Bi?directional LSTM recurrent neural network for Chinese word segmentation [C]// 2016 International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 345?353.
[11] STRUBELL E, VERGA P, BELANGER D, et al. Fast and accurate entity recognition with iterated dilated convolutions [C]// Proceedings of 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. [S.l.: s.n.], 2017: 2664?2669.
- 新课改下如何做好小学班主任工作
- 小学毕业班班级管理经验谈
- 提升儿童音乐合唱教学的有效性探讨
- 浅谈怎样培养学生的创新精神
- 大班音乐活动:舞被狮
- 小学英语口语交际能力的培养研究
- 全学段小学英语课程设计实践
- 小学数学课堂教学中的动手实践操作探讨
- 小学数学“统计与概率”教学中的问题分析
- 小学数学生活化教学初探
- 赣教云平台让低年级数学课堂绽放光芒
- 数学课堂与教育资源云平台的“鱼水之欢”
- 运用赣教云平台网络学习空间促进数学和创新创客的深度融合
- 赣教云平台与数学备课的深度融合
- 依托赣教云平台开展数学区域教研实践
- 《小数的初步认识》的教学策略分析
- “重”2“轻”5,以此类推而省之
- 浅析小学数学生活化教学
- 浅议导学案在小学数学教学中的有效运用
- 微课教学在小学数学课堂中的运用研究
- 浅谈数学教学中如何培养学困生学习兴趣
- 浅谈小学数学教学中学困生的转化工作
- 数学课如何培养学生的探究精神
- 微课在小学数学课堂教学中的应用策略
- 小学生数学阅读能力的培养
- reproofs
- reproof's
- reproportion
- reproportioned
- reproportioning
- reproportions
- repropose
- re-propose
- reproposed
- reproposes
- reproposing
- reprosecute
- reprosecuted
- reprosecutes
- reprosecuting
- reprotest
- reprotested
- reprotesting
- reprotests
- reprove
- reproved
- reprover
- reprovers
- reproves
- reproving
- 焚燎
- 焚燔
- 焚爇
- 焚琴煮鹤
- 焚琴鬻鹤
- 焚盥
- 焚研
- 焚砚
- 焚祷
- 焚稿
- 焚笔研
- 焚笔砚
- 焚纸
- 焚膏
- 焚膏油以继晷,恒兀兀以穷年
- 焚膏继晷
- 焚舟
- 焚舟济河
- 焚舟破釜
- 焚芝
- 焚荐
- 焚荡
- 焚萧
- 焚薙
- 焚薮而田