王华德,桑运春
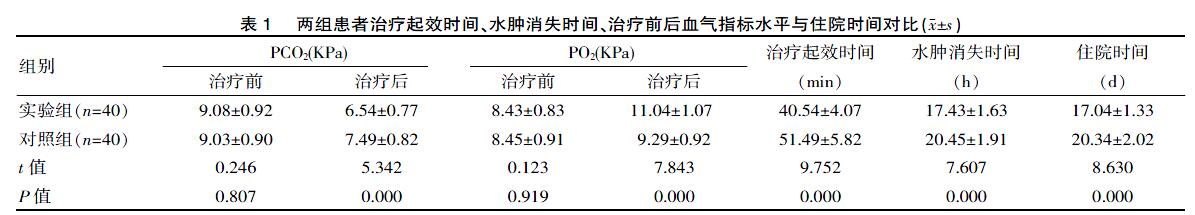
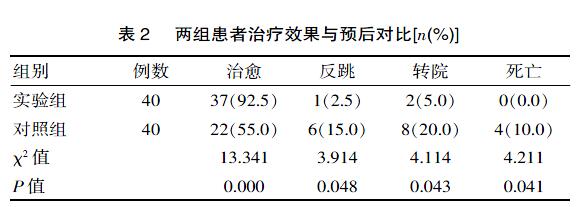
[摘要] 目的 觀察东茛菪碱与地塞米松联合治疗在急性中毒性肺水肿抢救中的临床分析。方法 方便选取该院2016年1月—2018年12月期间收治的急性中毒性肺水肿患者行常规治疗配合东茛菪碱与地塞米松联合抢救总计80例,随机分为观察组和对照组。通过观察两组患者治疗时治疗起效时间、水肿消失时间、治疗前后血气指标水平与住院时间,治疗效果与预后。结果 经治后实验组患者血气指标水平明显优于对照组,而实验组患者治疗起效时间、水肿消失时间与住院时间明显少于对照组,实验组与对照组患者治愈率(92.5% vs 55.0%),反跳率(2.5% vs 15.0%),转院率(5.0% vs 20.0%),死亡率(0.0% vs 10.0%),差异有统计学意义(t=9.752, P=0.000; t=7.607, P=0.000,t=0.246, P=0.807; t=5.342, P=0.000; t=0.123, P=0.919;t=7.843, P=0.000;t=8.630, P=0.000;χ2=13.341, P=0.000; χ2=3.914, P=0.048; χ2=4.114, P=0.043; χ2=4.211, P=0.041)。 结论 在急性中毒性肺水肿患者的抢救中,采取东茛菪碱与地塞米松联合治疗,可明显缩短患者治疗起效时间与水肿消失时间,提高临床救治效果。
[关键词] 东茛菪碱;地塞米松;联合治疗;急性中毒性肺水肿;抢救效果
[中图分类号] R595 ? ? ? ? ?[文献标识码] A ? ? ? ? ?[文章编号] 1674-0742(2020)02(a)-0112-03
Clinical Analysis of Combined Treatment of Scopolamine and Dexame thasone in Acute Toxic Pulmonary Edema
WANG Hua-de, SANG Yun-chun
Department of General Surgery, Feixian People's Hospital, Linyi, Shandong Province, 273400 ?China
[Abstract] Objective To observe the clinical analysis of the combined treatment of scopolamine and dexamethasone in the rescue of acute toxic pulmonary edema. Methods Convenient selection of 80 patients who were admitted to the hospital recently from January 2016 to December 2018 for diagnosis of acute toxic pulmonary edema and received conventional treatment in combination with east hyosamine and dexamethasone were randomly divided into the observation group and the control group. By observing the treatment onset time, edema disappearance time, blood gas index level and hospital stay before and after treatment, the treatment effect and prognosis of the two groups of patients. Results After treatment group was better than control group, patients with blood gas index level and effect of the experimental group patients, edema disappeared time and hospitalization time significantly less than the control group, experimental group and control group cure rate (92.5% vs 55.0%) patients, bounce rate (2.5% vs 15.0%), transfer rate(5.0% vs 20.0%), mortality (0.0% vs 10.0%), statistically significant difference (t=9.752, P=0.000; t=7.607, P=0.000,t=0.246, P=0.807; t=5.342, P=0.000; t=0.123, P=0.919;t=7.843, P=0.000;t=8.630, P=0.000;χ2=13.341, P=0.000; χ2=3.914, P=0.048; χ2=4.114, P=0.043; χ2=4.211, P=0.041). Conclusion In the rescue of patients with acute toxic pulmonary edema, the combination of scopolamine and dexamethasone can significantly shorten the onset time of treatment and the disappearance time of edema, and improve the clinical treatment effect.
该研究中,经治后实验组患者血气指标水平明显优于对照组,而实验组患者治疗起效时间、水肿消失时间与住院时间明显少于对照组,实验组与对照组患者治愈率(92.5% vs 55.0%),反跳率(2.5% vs 15.0%),转院率(5.0% vs 20.0%),死亡率(0.0% vs 10.0%),差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
综上所述,在急性中毒性肺水肿患者的抢救中,采取东茛菪碱与地塞米松联合治疗,可明显缩短患者治疗起效时间与水肿消失时间,提高临床救治效果,改善患者血气指标及预后,并缩短住院时间,间接减轻患者及家属经济负担,效果理想。
[参考文献]
[1] ?丁毅. 托拉塞米注射液联合机械通气+PEEP 治疗重症急性肺水肿疗效分析[J].中国急救医学,2016,36(1):234- 235.
[2] ?Ewa WS,Wierszcz Jolanta,Andrzej S.Effects of Atorvastatin Dose and Concomitant Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors on Renal Function Changes over Time in Patients with Stable Coronary Artery Disease: A Prospective Observational Study[J].International Journal of Molecular Scien ces,2016,17 (2): 106-109 .
[3] ?徐刚, 董芳, 董碧華,等. 机械通气治疗急性心肌梗死合并急性肺水肿的临床效果[J].实用临床医药杂志, 2016, 20(3):7-10.
[4] ?Bao -Jia LI,Quan MO,Shi GJ,et al. Study on the application value of percutaneous dilational tracheostomy on the rescue of patients with severe cerebrovascular accident[J].China Modern Medicine,2016(21):50-53.
[5] ?孟瑶. 急性心肌梗死合并急性肺水肿应用机械通气辅助治疗的效果观察[J].中国煤炭工业医学杂志,2015,18 (10):1639-1642.
[6] ?罗晓红,郭文静,许瑞元,等.模拟不同海拔低氧对大鼠下丘脑-垂体-甲状腺轴及肺组织 VEGF和 HIF-1表达的影响[J].解放军医学院学报,2016,37(8):864-868.
[7] ?申强, 吴铁军, 王国青. 机械通气治疗急性心肌梗死并急性肺水肿的临床效果观察[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志, 2016, 22(8):147-148.
[8] ?陆启光.参附注射液联合有创机械通气治疗急性心源性肺水肿的临床效果分析[J].中华中医药学刊,2015,17(6):1533-1536.
[9] ?蒙萍,王宁,漆欣柱,等.模拟海拔8 000m 高原缺氧环境对大鼠脑组织线粒体自噬的影响[J].解放军医药杂志,2016, 28(6):9-13.
[10] ?季一娟, 单红卫, 巢益群,等. 有创-无创序贯机械通气对急性心源性肺水肿患者低氧血症和血流动力学的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2016, 16(29):5651-5654.
(收稿日期:2019-11-04)
- 档案管理实施信息化相对于人力管理的优势
- 档案信息化建设中出现的诸多问题和应对策略
- “物哀”文化视角下日本人的身份建构
- 试论图书资料管理工作的路径优化
- 浅析茨威格笔下女性情感的无私奉献
- 档案信息化数据入库的规范化
- 档案信息化建设进程中的数字化模式
- 档案信息化建设之电子档案数据库的建立
- 基于无纸化办公的档案信息化管理的必要性分析
- 浅析档案信息化的重要性
- 档案信息化之电子文件归档与管理
- 依托课堂观察,论美术课堂中有效提问的实效性
- 档案信息化管理的优化建议与提效路径
- 作品鉴赏(1)
- 作品鉴赏
- 自动化控制技术在煤矿通风系统中的应用
- 商务英语谈判技巧在国际经济贸易发展中的应用研究
- 浅谈高中英语课堂互动模式的实践与研究
- 农产品品质劣变在线探测技术研究
- 基于行动研究的英语教师课堂教学对策探析
- 以规划落实产业用地促进传统产业转型升级
- 基于新城市社会学视角下我国当代城市空间的研究
- 广告创收与经营机制创新分析
- 浅谈如何提升烟草行业创新工作质量
- 刍议离退休职工管理服务工作现状及对策
- indivisibles
- indivisibly
- indoctrinate
- indoctrinated
- indoctrinates
- indoctrinating
- indoctrination
- indoctrinations
- indoctrinator
- indoctrinators
- indolence
- indolent
- indolently
- indomitabilities
- indomitability , indomitableness
- indomitable
- indomitablenesses
- indomitably
- indoor
- indoors
- indorse
- indorsement
- in doubt
- in dribs and drabs
- in droves
- 珍珠婚
- 珍珠宝石一类的装饰品
- 珍珠少个眼儿——再光滑也是瞎宝
- 珍珠挂在颈上,友谊嵌在心上
- 珍珠换绿珠
- 珍珠掺着绿豆卖
- 珍珠掺着绿豆卖——一样价钱也抱屈
- 珍珠掺着绿豆卖,一样价钱也抱屈
- 珍珠散
- 珍珠没眼儿——瞎宝贝
- 珍珠港
- 珍珠港事件
- 珍珠玛瑙都出在鳖身上
- 珍珠的一种
- 珍珠的光彩
- 珍珠的故乡
- 珍珠笋
- 珍珠等宝物
- 珍珠米
- 珍珠缀成的帘子
- 珍珠美玉
- 珍珠落在粪堆上——没人赏识
- 珍珠蒙尘不放光
- 珍珠贝
- 珍瑞