石智勇 侯念果 李会 帅训军 杨洪光 孙常荣 路文卿 艾登斌

[摘要]目的 探讨骨髓间充质干细胞(BMSCs)减缓大鼠急性肺损伤(ALI)的机制。方法 36只6~7周龄雄性SD大鼠适应性饲养1周后,随机取12只作为对照组(Con组),其余大鼠均经尾静脉注射脂多糖(LPS)制作大鼠急性肺损伤模型。若大鼠模型的氧合指数(PaO2/FiO2)<300 mmHg,肺组织病理学评分升高,湿重(W)/干重(D)值升高,提示造模成功。将模型大鼠随机分为模型组(ALI组)和治疗组(BMSCs组),每组12只。BMSCs组造模1 h后气管内注射100 μl BMSCs悬浮液(细胞总数为5×106),Con组和ALI组气管内注射100 μl 0.9%生理盐水。24 h后腹主动脉置入导管抽取动脉血测定血氧分压(PaO2)并计算PaO2/FiO2;取肺组织行病理学评分、測量W/D;酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中肿瘤坏死因子-α(TNF-α)、白细胞介素-1α(IL-1α)、白细胞介素-10(IL-10)水平;采用血细胞计数仪测定中性粒细胞数(PMN);蛋白免疫印迹法(Western-Blot)测定肺组织中Bcl-2、Bax、Caspase-3蛋白的表达,并计算Bcl-2/Bax。比较三组大鼠的PaO2/FiO2、W/D、肺组织病理学评分、TNF-α、IL-1α、IL-10、PMN、Caspase-3、Bcl-2、Bax及Bcl-2/Bax水平。结果 ALI组和BMSCs组的W/D、肺组织病理学评分、TNF-α、IL-1α、IL-10水平、PMN数目、Caspase-3蛋白、Bax蛋白的表达高于Con组,PaO2/FiO2、Bcl-2蛋白表达、Bcl-2/Bax低于Con组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);BMSCs组的W/D、肺组织病理学评分、TNF-α、IL-1α、PMN数目、Caspase-3蛋白及Bax蛋白表达低于ALI组,IL-10水平、PaO2/FiO2、Bcl-2蛋白及Bcl-2/Bax高于ALI组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 BMSCs可抑制大鼠ALI模型的肺组织细胞凋亡,其机制可能与上调了肺组织中的Bcl-2蛋白和下调了Bax蛋白和Caspase-3蛋白的表达有关。
[关键词]骨髓间充质干细胞;急性肺损伤;脂多糖;凋亡
[中图分类号] R563? ? ? ? ? [文献标识码] A? ? ? ? ? [文章编号] 1674-4721(2019)10(b)-0011-05
[Abstract] Objective To explore the mechanism of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) in alleviating acute lung injury (ALI) in rats. Methods Thirty-six male SD rats aged 6-7 weeks were fed for one week. Twelve rats were randomly selected as control group (Con group), the other rats were injected with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via caudal vein to establish acute lung injury model. If the oxygenation index (PaO2/FiO2)<300 mmHg, the pathological score of lung tissue increased, and the wet weight (W)/dry weight (D) value increased, suggesting that the model was successful. The model rats were randomly divided into model group (ALI group) and treatment group (BMSCs group), with 12 rats in each group. In BMSCs group, 100 ml BMSCs suspension was injected into the trachea after 1 hour of modeling (the total number of cells was 5×106), 100 ml 0.9% saline was injected into the trachea of Con group and ALI group. After 24 hours, the abdominal aorta was inserted with a catheter to extract arterial blood and the partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) was measured and PaO2/FiO2 was calculated. The lung tissues were taken for pathological scoring and W/D was measured. The levels of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), interleukin-1α (IL-1α) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were detected by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The number of neutrophils (PMN) was measured by blood cell counting instrument. The expression of Bcl-2 protein, Bax protein and Caspase-3 protein in lung tissue was determined by Western-Blot, and the expression of Bcl-2/Bax was calculated. The levels of PaO2/FiO2, W/D, lung histopathological score, TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-10, PMN, Caspase-3, Bcl-2, Bax and Bcl-2/Bax were compared among the three groups. Results The W/D, lung histopathological score, TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-10, PMN number, Caspase-3 protein and Bax protein expression in ALI group and BMSCs group were higher than those in Con group, while PaO2/FiO2, Bcl-2 protein expression and Bcl-2/Bax protein expression were lower than those in Con group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The W/D, lung histopathological score, TNF-α, IL-1α, PMN number, Caspase-3 protein and Bax protein expression in BMSCs group were lower than those in ALI group, IL-10 level, PaO2/FiO2, Bcl-2 protein and Bcl-2/Bax in BMSCs group were higher than those in ALI group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion BMSCs can inhibit apoptosis of lung tissue in rat ALI model, which may be related to up-regulation of Bcl-2 protein and down-regulation of Bax protein and Caspase-3 protein expression in lung tissue.
1.5统计学方法
采用统计学软件SPSS 19.0分析数据,计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较采用t检验;计数资料以率表示,采用χ2检验,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
2.1三组大鼠PaO2/FiO2、W/D及肺组织病理学评分的比较
三组大鼠的PaO2/FiO2、W/D及肺组织病理学评分比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001);ALI组和BMSCs组大鼠的PaO2/FiO2低于Con组,W/D和肺组织病理学评分高于Con组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);BMSCs组大鼠的PaO2/FiO2高于ALI组,W/D和肺组织病理学评分低于ALI组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表1)。
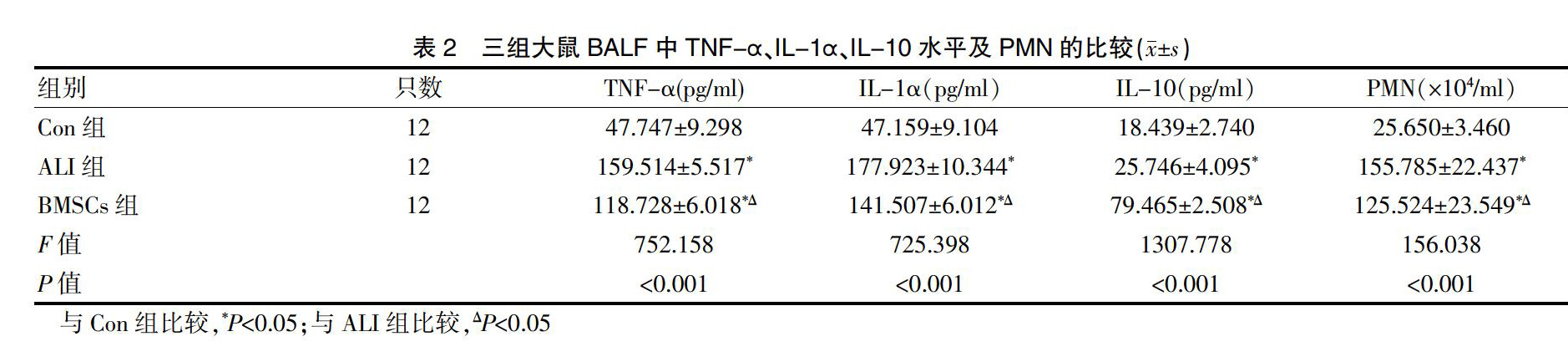
2.2三组大鼠BALF中TNF-α、IL-1α、IL-10水平及PMN的比较
三组大鼠BALF中的TNF-α、IL-1α、IL-10水平及PMN比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001);ALI组和BMSCs组大鼠BALF中的TNF-α、IL-1α,IL-10水平及PMN均高于Con组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);BMSCs组大鼠BALF中的TNF-α、IL-1α,PMN低于ALI组,IL-10水平高于ALI组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表2)。
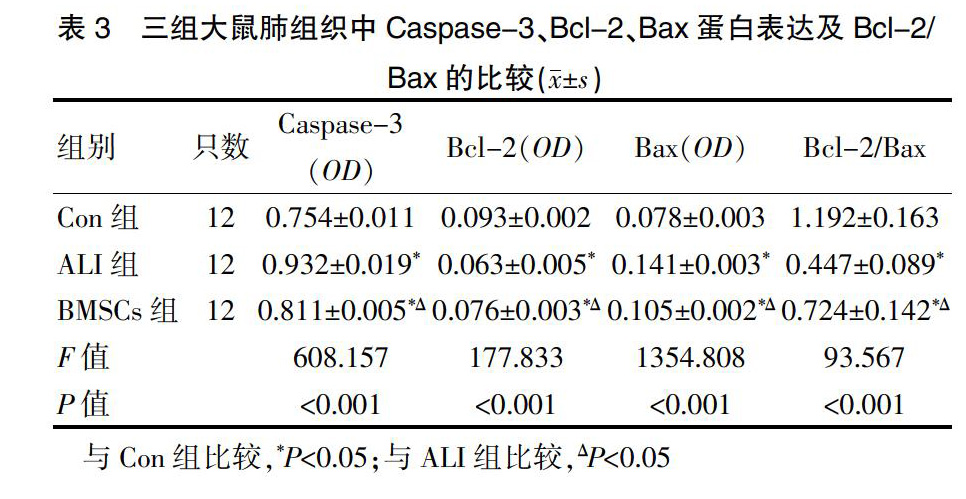
2.3三组大鼠肺组织中Caspase-3、Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达及Bcl-2/Bax的比较
三组大鼠组织中的Caspase-3、Bcl-2、Bax蛋白表达及Bcl-2/Bax比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.001);ALI组和BMSCs组大鼠组织中的Caspase-3、Bax蛋白表达高于Con组,Bcl-2蛋白表达和Bcl-2/Bax低于Con组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);BMSCs组大鼠的肺组织中Caspase-3、Bax蛋白表达低于ALI组,Bcl-2蛋白表达及Bcl-2/Bax高于ALI组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)(表3)。
3讨论
临床上ALI以肺容积减少,肺顺应性降低、通气/血流比例失调为病理生理特点,主要表现为进行性低氧血症和呼吸窘迫。本实验中,给予LPS后的ALI组与Con组比较,其PaO2/FiO2下降,肺组织病理学评分升高,W/D值升高,提示造模成功;给予BMSCs的BMSCs组与ALI组比较,PaO2/FiO2上升,肺组织病理学评分下降,W/D值降低,提示BMSCs能缓解ALI所致的肺组织病理损伤,改善动脉血氧分压。
研究显示,ALI发病机制十分复杂,如炎性反应损伤、细胞凋亡损伤、凝血与纤溶系统失衡损伤、氧化还原失衡损伤等[9]。大量研究显示,炎症反应-抗炎反应失衡是ALI、ARDS的主要发病机制,即IL-10等抗炎因子分泌不足,TNF-α、IL-1α促炎因子分泌增多[10]。本实验结果显示,ALI组和BMSCs组大鼠BALF中的TNF-α、IL-1α及IL-10水平均高于Con组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);BMSCs组大鼠BALF中的TNF-α、IL-1α,PMN低于ALI组,IL-10水平高于ALI组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示BMSCs能够减轻ALI炎性因子的表达。
PMN是ALI发病机制中的关键效应细胞[11],炎症发生时,PMN因炎性因子、脂质介质、微环境的变化作为第一响应者向炎性区域聚集[12-13],并释放大量蛋白酶、氧自由基等破坏肺泡上皮细胞和肺毛细血管内皮细胞。ALI早期PMN凋亡延迟,同时对其他PMN产生趋化作用,引起更多的PMN聚集来破坏细胞。本实验结果显示,ALI组和BMSCs组大鼠BALF中的PMN高于Con组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);BMSCs组大鼠BALF中的PMN低于ALI组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。提示BMSCs能减少ALI时炎性细胞PMN在肺内聚集、浸润。
炎症反应是ALI重要的发病机制,Soliman等[14-15]大部分学者也将ALI治疗方法的研究重点放在了抑制炎症的发生上面,但越来越多的研究显示细胞凋亡在ALI中发挥着重要作用。ALI产生的细胞因子可能抑制了炎症细胞的凋亡,从而延长了炎性反应的过程,促进了肺泡上皮细胞的凋亡,加重了肺泡及毛细血管的损伤[16],这些损伤性刺激又进一步诱发了细胞凋亡。Koh等[17]通过LPS刺激人肺動脉内皮细胞,检测到了凋亡前体蛋白Caspase-3、Bax的表达均明显增强,这些蛋白表达的增加与肺血管内皮细胞的凋亡增加一致。ALI时,肺组织产生的TNF-α、IL-1α等炎性因子诱导了肺泡上皮细胞凋亡,在此过程中,Caspase-3作为最重要的凋亡执行者,一旦活化,标志着凋亡进入不可逆阶段[18]。本实验结果显示,ALI组和BMSCs组大鼠组织中的Caspase-3蛋白表达均高于Con组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),提示ALI发生时出现了细胞凋亡;BMSCs组大鼠的肺组织中Caspase-3蛋白表达低于ALI组,提示BMSCs可能减缓了凋亡的发生。
Caspase-3作为下游的凋亡执行蛋白,同时受到上游凋亡调控蛋白的影响;促凋亡蛋白Bax,主要介导线粒体内部分子进入细胞质[19]激活Caspase-3;Bcl-2是调控蛋白中重要的抗凋亡蛋白,Bcl-2蛋白表达水平的下降可能会导致细胞凋亡[20]。Bcl-2直接决定了细胞是存活还是凋亡[21],当比值上升时,凋亡受到了抑制,反之则促进了凋亡的发生。本实验结果显示,ALI组和BMSCs组大鼠组织中的Bax蛋白表达高于Con组,Bcl-2蛋白表达和Bcl-2/Bax低于Con组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),提示ALI中细胞凋亡参与细胞损伤,且肺损伤促进了细胞凋亡;BMSCs组大鼠的肺组织中Bax蛋白表达低于ALI组,Bcl-2蛋白表达及Bcl-2//ax高于ALI组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),提示BMSCs可抑制ALI所致的细胞凋亡,且通过上调Bcl-2表达,下调Bax蛋白的表达。
综上所述,BMSCs可抑制大鼠ALI模型的肺组织细胞凋亡,其机制可能与上调了肺组织中Bcl-2蛋白和下调Bax蛋白、Caspase-3蛋白的表达有关,为治疗ALI提供了新的思路。
[参考文献]
[1]Bellani G,Laffey JG,Pham T,et al.Epidemiology,patterns of care,and mortality for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome in intensive care units in 50 countries[J].JAMA,2016,315(8):788-800.
[2]Pham T,Rubenfeld GD.The epidemiology of acute respiratory distress syndrome a 50th birthday review[J].Am J Respir Crit Care Med,2017,195(7):860-870.
[3]Tang PS,Marco M,Seth R,et al.Acute lung injury and cell death:how many ways can cells die?[J].Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol,2008,294(4):L632-L641.
[4]Friedenstein AJ,Petrakova KV,Kurolesova AI,et al.Heterotopic of bone marrow.Analysis of precursor cells for osteogenic and hematopoietic tissues[J].Transplantation,1968,6(2):230-247.
[5]Yagi H,Soto-Gutierrez A,Kitagawa Y,et al.Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate organ injury induced by LPS and burn[J].Cell Transplant,2010,19(6):823-830.
[6]贺争鸣,李根平,李冠民,等.实验动物福利与动物实验科学[M].北京:科学出版社,2011.
[7]罗友,吴欣瞳,庞欣欣,等.小鼠急性肺损伤造模条件的探究[J].中国畜牧兽医,2017,44(8):2269-2276.
[8]Matute-Bello G,Downey G,Moore BB,et al.An official american thoracic society workshop report:features and measurements of experimental acute lung injury in animals[J].Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol,2011,44(5):725-738.
[9]马李杰,李王平,金发光.急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制的研究进展[J].中华肺部疾病杂志(电子版),2013,6(1):65-68.
[10]汲海燕.急性肺损伤/急性呼吸窘迫综合征发病机制的研究进展[J].吉林医学,2014,35(29):6578-6579.
[11]Rebetz J,Semple JW,Kapur R.The pathogenic involvement of neutrophils in acute respiratory distress syndrome and transfusion-related acute lung injury[J].Transfus Med Hemother,2018,45(5):290-298.
[12]Sadik CD,Luster AD.Lipid-cytokine-chemokine cascades orchestrate leukocyte recruitment in inflammation[J].J Leukoc Biol,2012,91(2):207-215.
[13]Mócsai,A,Walzog B,Lowell CA.Intracellular signalling during neutrophil recruitment[J].Cardiovasc Res,2015,107(3):373-385.
[14]Soliman MG,Mansour HA,Hassan WA,et al.Mesenchymal stem cells therapeutic potential alleviate lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rat model[J].J Biochem Mol Toxicol,2018,32(11):e22217.
[15]Kim ES,Chang YS,Choi SJ,et al.Intratracheal transplantation of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates Escherichia coli-induced acute lung injury in mice[J].Respir Res,2011,12(1):108.
[16]邬娇,郭曲练.急性肺损伤与细胞凋亡[J].中日友好医院学报,2009,23(2):117-119.
[17]Koh H,Tasaka S,Hasegawa N,et al.Protective role of vascular endothelial growth factor in endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in mice[J].Respir Res,2007,8(1):60.
[18]Cryns V,Yuan J.Proteases to die for[J].Genes Dev,1998,12(11):1551-1570.
[19]Munoz-Pinedo C,Guío-Carrión A,Goldstein JC,et al.Different mitochondrial intermembrane space proteins are released during apoptosis in a manner that is coordinately initiated but can vary in duration[J].Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2006,103(31):11 573-11 578.
[20]Chopra M,Reuben JS,Sharma AC.Acute Lung Injury:Apoptosis and Signaling Mechanisms[J].Exp Biol Med (Maywood),2009,234(4):361-371.
[21]Tsukahara S,Yamamoto S,Shwe TTW,et al.Inhalation of low-level formaldehyde increases the Bcl-2/Bax expression ratio in the hippocampus of immunologically sensitized mice[J].Neuroimmunomodulation,2006,13(2):63-68.
(收稿日期:2019-05-31? 本文編辑:刘克明)
- 碰撞过程“熵”的变化探究
- 一种风力发电机组冷却风机隔振器的选型设计
- 带二级密勒补偿的运算放大器研究
- 永磁直驱风力发电机组的防雷接地保护探讨
- 城市轨道交通车辆样车的研发试制
- 基于Kinect与ARToolkit增强现实的遮挡一致性算法研究
- 时效热处理工艺对Al-Zn-Mg合金材料组织与腐蚀性能的影响
- 改进关键链挣值技术在软件工程及集成项目进度控制中运用探讨
- “互联网+”视域下扶绥稻秆画创新发展之路
- 基于金融监管角度的P2P平台规范发展探讨
- 新零售背景下连锁企业店铺开发布局策略研究
- 企业内部沟通机制分析
- 大数据时代电商企业网络口碑危机预警研究
- 新生代卷烟消费体验评价指标体系构建研究
- 互联网企业并购研究
- 我国医药电商企业战略分析
- 传统手工艺次代五维化研究
- 电子商务对传统商业模式的影响分析
- 东营涉海工业企业发展困境研究
- 有限公司增资时股东对放弃份额优先认购问题探讨
- 建设银行信贷资产证券化对其经营绩效的影响
- 新审计报告中的关键审计事项探究
- 董事会特征与审计质量的关系研究
- 营运中的农村基础设施资产绩效管理研究
- 商业银行P2P资金存管业务的风险控制分析
- unadulatory
- unadult
- unadulterate
- unadulterated
- unadulteratedly
- unadvancing
- unadvantageously
- unadvantageousness
- unadvantageousnesses
- unadventuring
- unadventurously
- unadventurousness
- unadventurousnesses
- unadverse
- unadversely
- unadverseness
- unadversenesses
- unadvisableness
- unadvisablenesses
- unadvisably
- unadvocated
- unaerated
- unaffable
- unaffableness
- unaffablenesses
- 长篇小说——千言万语
- 长篇小说的创作
- 长篇小说的结构
- 长篇的书面意见
- 长篇累牍
- 长篇连载
- 长籍
- 长素
- 长红
- 长约一指
- 长纶
- 长线
- 长线产品
- 长线工程
- 长线投资
- 长线放远风筝——下过大功夫
- 长线放远鹞
- 长线放远鹞儿。
- 长线放风筝
- 长线红娘
- 长线资金
- 长终
- 长绒棉
- 长结
- 长绝