乔冠恩 孔洪彬 王敏 李亮亮 朱琳 董魁 张文娟 马立东
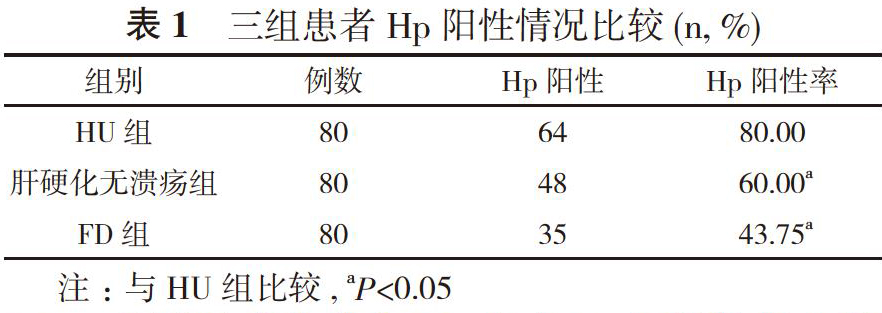
【摘要】 目的 研究肝源性溃疡(HU)患者幽门螺杆菌(Hp)感染情况及影响因素。方法 选取确诊的80例HU患者作为HU组, 80例肝硬化无消化性溃疡患者作为肝硬化无溃疡组, 80例功能性消化不良(FD)患者作为FD组, 通过快速尿素酶试验(RUT)或14C尿素呼气试验来判断Hp感染。比较三组患者Hp阳性情况;不同肝功能分级、不同食管静脉曲张程度HU患者Hp阳性情况。结果 HU组患者Hp阳性率为80.00%, 明显高于肝硬化无溃疡组的60.00%、FD组的43.75%, 差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。80例HU患者中, 肝功能A级患者Hp阳性率为79.17%(38/48), 与肝功能B级的81.25%(26/32)比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。80例HU患者中, 轻度食管静脉曲张患者Hp阳性率为88.89%(40/45), 高于中重度食管静脉曲张患者的68.57%(24/35), 差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 HU患者有较高的Hp感染率, Hp感染是HU患者发病原因之一, 且Hp感染与HU患者门脉压有关, 与肝功能分级无关。
【关键词】 肝源性溃疡;发病机制;幽门螺杆菌
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2020.12.008
【Abstract】 Objective? ?To study Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infection and its influencing factors in patients with hepatogenic ulcer (HU). Methods? ?There were 80 confirmed HU patients selected as the HU group,?80 patients with cirrhosis without peptic ulcers as the cirrhosis without ulcers group, and 80 patients with functional dyspepsia (FD) as the FD group. HP infection was determined by rapid urease test (RUT) or 14C urea breath test. The Hp-positive status and Hp-positive status of HU patients with different liver function grades and different degrees of esophageal varices were compared among three groups of patients. Results? ?The Hp-positive rate of HU group was 80.00%, which was obviously higher than that of cirrhosis without ulcers group 60.00% and FD group 43.75%, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). In 80 HU patients, the HP-positive?rate was 79.17% (38/48) in patients with grade A liver function, and there was no statistically significant difference compared with 81.25% (26/32) in patients with grade B liver function (P>0.05). In 80 HU patients, the?HP-positive rate of mild esophageal varices was 88.89% (40/45), which was higher than that of moderate and severe esophageal varices 68.57% (24 / 35), and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion? There is a in HU patients. Hp infection is one of the causes of HU patients, and Hp infection is correlated with portal pressure in HU patients and has nothing to do with liver function grades.
【Key words】 Hepatogenic ulcer; Pathogenesis; Helicobacter pylori
肝源性潰疡(hepatogenic ulcer, HU)是指在肝硬化基础上发生的消化性溃疡, 是肝硬化上消化道出血的常见原因, 其症状常为肝硬化本身表现所掩盖, 多表现为无规律的上腹痛、反酸、嗳气、腹胀、纳差等, 病程长, 不易愈合, 容易漏诊、误诊, 一般的抑酸治疗难以取得令人满意的效果, 长期以来是临床治疗的难题。HU的发病机制和普通消化性溃疡不完全相同, 与门静脉高压、肝功能损害等因素有关, 但确切机制尚不清楚, 尤其关于幽门螺杆菌(Hp)是否是HU的病因, 目前还存在很大争议[1-3]。为此, 本文对2010年1月~2019年12月收治的经确诊的80例HU患者、肝硬化非溃疡患者及FD患者进行Hp感染情况调查, 以期阐明二者的相关性, 现报告如下。
对HU患者Hp感染的影响因素进行分析, 本研究观察了HU患者的肝功能及食管静脉曲张情况对Hp的影响, 结果显示, Hp感染与HU患者的肝功能分级无明显相关, 而与其食管静脉曲张程度呈负相关, 说明Hp感染与HU患者的门脉高压有关, 与肝功能分级无关, 此结果与以前有关研究一致[9-11]。
综上所述, HU患者有较高的Hp感染率, Hp感染是HU患者发病原因之一, 且Hp感染与HU患者门脉压有关, 与肝功能分级无关。
参考文献
[1] Voulgaris T, Karagiannakis D, Siakavellas S, et al. High prevalence of asymptomatic peptic ulcers diagnosed during screening endoscopy in patients with cirrhosis. Ann Gastroenterol, 2019, 32(5):451-456.
[2] 张绍敏, 邹湉, 付小义, 等. 乙型肝炎后肝硬化合并消化性溃疡与幽门螺杆菌感染的相关性. 中国肝脏病杂志(电子版), 2016, 8(4):48-51.
[3] Vergara M, Calvet X, Roqué M. Helicobacter pylori is a risk factor for peptic ulcer disease in cirrhotic patients. A meta-analysis. European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 2002, 14(7):717-722.
[4] 張亚辉, 张丽艳, 欧阳义, 等. 肝硬化合并消化性溃疡内镜特点及与门静脉高压的关系. 中国现代医药杂志, 2015(1):70-71.
[5] Nolan JP. The role of intestinal endotoxin in liver injury: A long and evolving history. Hepatology, 2010, 52(5):1829-1835.
[6] 贾昊鹍, 王正根. 肝源性溃疡的发病机制与药物治疗. 中南医学科学杂志, 2017, 45(2):201-203.
[7] 龙会宝, 王连源. 肝源性溃疡的临床研究现状. 新医学, 2008, 39(2):137-138, 140.
[8] 龙会宝, 陈玉成, 王连源. 肝硬化与肝源性溃疡及幽门螺杆菌感染的临床研究. 岭南急诊医学杂志, 2009, 14(6):445-446, 449.
[9] Miglioli M, Corinaldesi R, Bolondi L, et al. High Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori in Liver Cirrhosis (Relationship with Clinical and Endoscopic Features and the Risk of Peptic Ulcer). digestive diseases & sciences, 1997, 42(10):2024-2030.
[10] 程八五, 钟能华. 肝源性溃疡患者幽门螺杆菌感染分析. 安徽医学, 2001, 22(4):41-42.
[11] 乔冠恩, 车筑萍, 谭庆华, 等. 肝硬化与幽门螺杆菌关系的临床研究. 贵阳医学院学报, 2004, 29(2):105-107.
[收稿日期:2020-02-17]
- 二灰结石基层配合比设计及施工方法的探讨
- 浅析建筑外墙保温施工技术与施工措施
- 中国企业跨境并购的策略分析
- 高速公路双连拱隧道施工信息化管理技术
- 对企业财务重述概念的解析及其监管
- 浅谈鹤壁煤化工回填土的强夯法地基处理
- 埃塞俄比亚FAN电站机组移交程序的总结与分析
- 投标策略与技巧探讨
- “流动科技馆县县通”工程的运行与思考
- 会税差异与产权性质对会计稳健性的影响
- 浅谈“无功补偿”与“力率电费”
- X6132纵向垂直数控改造
- 浅析工业企业用电的无功功率补偿
- SF6断路器故障特点及检修维护
- 启动/备用变出线方式变更后相关保护情况
- 同程、去哪儿、携程网机票价格比较分析
- 洪水操舟机防沙改造中冷却器容积的设计
- 浅谈CAD技术在工程设计中的应用
- 玉米田化学除草剂合理使用
- 我国采矿工程对煤炭行业发展和安全的影响
- 常州市钟楼区楼宇经济发展问题研究
- MPW变频张紧绞车的应用
- 浅谈企业保卫部门在综合治理中如何发挥作用
- 对灵新煤矿运输专业风险预控体系的探讨
- 坚硬顶板大断面沿空留巷技术研究与应用
- unethereally
- unetherealness
- unetherealnesses
- unethical
- unethicalities
- unaccurately
- unaccurateness
- unaccuratenesses
- unaccursed
- unaccusable
- unaccusing
- unaccusingly
- unaccustom
- unaccustomed
- unaccustomedly
- unaccustomedness
- unaccustomednesses
- unaccustomed/unused to
- unaccustoming
- unaccustoms
- unachievable
- unachieved
- unaching
- unacidic
- unacknowledging
- 诗话
- 诗语
- 诗说
- 诗课
- 诗谛
- 诗谜
- 诗谜儿
- 诗谣
- 诗谱
- 诗谱南山
- 诗豪
- 诗豪酒圣
- 诗貌
- 诗账
- 诗贵情思而轻事实
- 诗贵有奇趣
- 诗贵有闲情
- 诗贵自然
- 诗赋
- 诗赋的状物与抒情
- 诗赋词曲概论
- 诗趣
- 诗轴
- 诗辞
- 诗辨坻